Castor bean crop
Ricinus communis, popularly known as castor bean, is a plant from the Euphorbiaceae family. It is the only species of the monotypic genus Ricinus belonging to the subtribe Ricininae.
Castor is native to the south-eastern Mediterranean basin, Eastern Africa, and India, although it is widespread throughout tropical regions.
Castor bean is the source of castor oil, which has a wide variety of uses. The beans contain a high percentage of oil rich in triglycerides, mainly ricinolein. The bean also contains ricin, a soluble toxin present in lower concentrations throughout the plant.


Castor bean oil
Castor oil is a vegetable oil extracted from the castor beans. It is a colorless to very pale- yellow liquid with a distinct taste and smell. Its boiling point is 313 °C (595 °F) and its density is 0.961 g / cm³. It is a triglyceride, in which approximately 90% of the fatty acid chains are ricinoleates. Oleate and linoleate are the other significant components.

Properties of Castor and its derivatives:
- Cold impact resistance;
- Ageing resistance;
- Chemical resistance;
- Abrasion resistance;
- Flexibility;
- Burst strength;
- Dimensional stability;
- Easy processing;
- Smooth surface finish;
- Lightweight;
- High and low temperature performance.
Castor oil – main uses
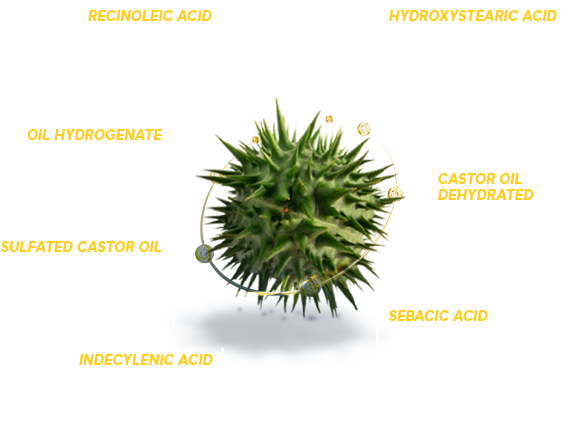
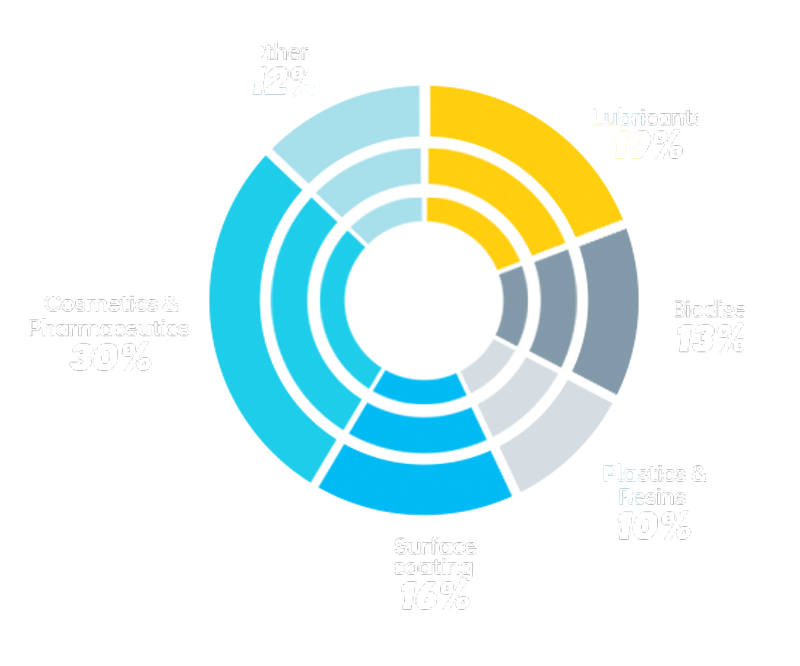
Uses of castor oil and its derivatives
Castor oil and its derivatives are used to manufacture soaps, lubricants, hydraulic and brake fluids, paints, dyes, coatings, cold-resistant plastics, nylon, textiles, footwear, sports equipment, pharmaceuticals, fragrances, food preservatives, skin and hair care, industrial chemical precursors, lubricants, biodiesel, among other products.

Market overview
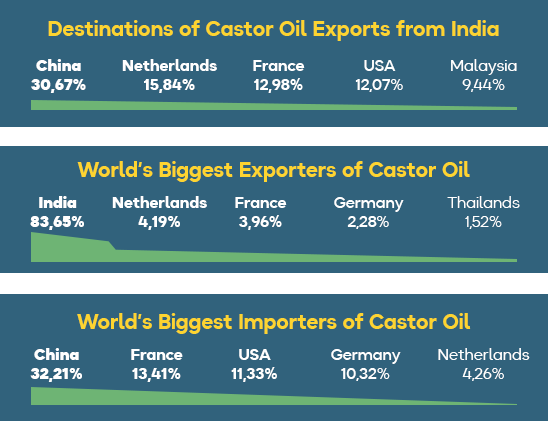
India is the world’s leading producer of castor beans and dominates the international trade in castor oil, supplying around 80% of global demand for this commodity. China and Brazil are the other major producers. China, the USA, the European Union and Japan are the main importers of castor bean oil.

Trading
Castor beans are commodity traded on the NCDEX – National Commodity & Derivatives Exchange.
NCDEX is a commodities exchange which deals primarily with agricultural commodities in India. The National Commodity & Derivatives Exchange was established in 2003, and its headquarters are in Mumbai (https://www.ncdex.com)
Castor bean market
(US$ billion) – Global
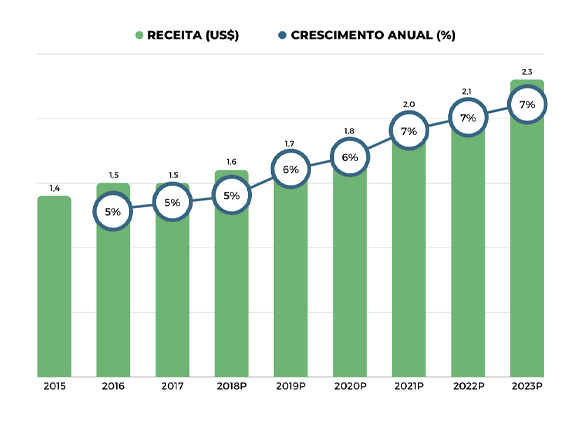
Global - demand